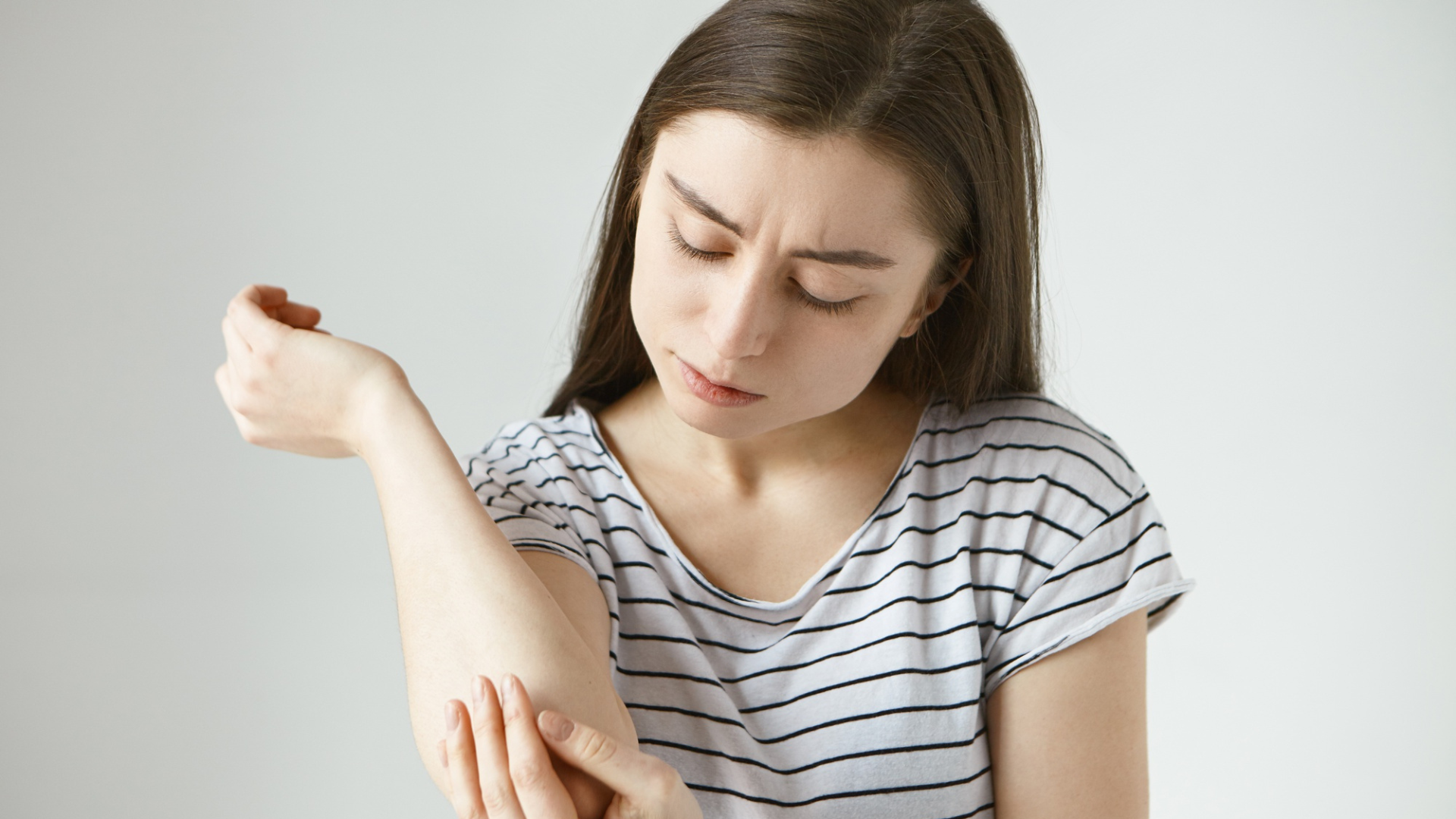

Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition that can appear suddenly and cause significant discomfort. It manifests as raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. While often a temporary and harmless reaction, the abrupt onset of urticaria can be alarming. Understanding its causes and knowing how to treat it quickly can provide much-needed relief and peace of mind. For those seeking professional guidance, specialized clinics like Touch Aesthetic Clinic offer expert care for various skin conditions.
Unraveling the Causes of Sudden Urticaria
Sudden urticaria, or acute urticaria, is a reaction of the body to a trigger that causes the release of histamine and other chemicals into the skin. This chemical release leads to inflammation and the characteristic hives. Identifying the specific trigger can sometimes be challenging, but common culprits include:
- Allergic Reactions: This is one of the most frequent causes of acute hives. Allergens can be found in certain foods like peanuts, shellfish, eggs, and milk. Medications, particularly antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen, are also common triggers. Insect stings or bites can also provoke an allergic response leading to urticaria.
- Infections: Both viral and bacterial infections can be a source of hives, especially in children. The common cold, flu, urinary tract infections, and strep throat are some examples of infections that can trigger an urticarial rash.
- Environmental Factors: For some individuals, physical stimuli can induce hives. This can include exposure to cold or heat, sunlight, water, and even pressure on the skin from tight clothing. Exercise and sweating can also be triggers for some people.
- Stress: Emotional stress is another factor that can contribute to the development of hives. While stress itself may not be the direct cause, it can exacerbate the body’s immune response and worsen symptoms.
The Appearance of Urticaria
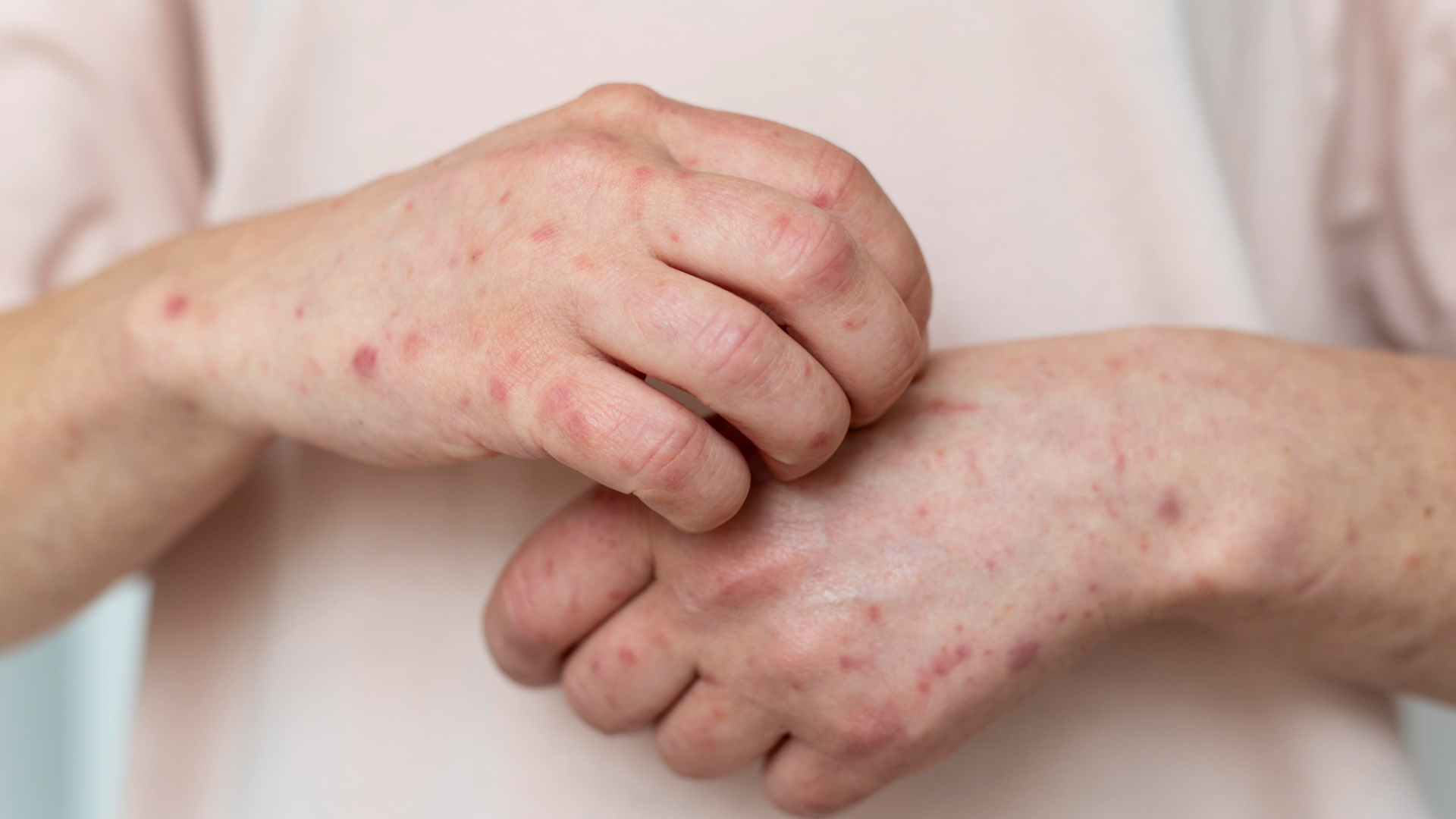
The primary symptom of urticaria is the appearance of wheals, which are raised, itchy bumps on the skin. These wheals can be red or skin-colored and often have a pale center when pressed. They can appear anywhere on the body and may vary in size from a few millimeters to several inches in diameter. The rash can be localized to one area or spread across a larger part of the body. A key characteristic of hives is that individual wheals typically disappear within 24 hours, though new ones may form.
In some cases, urticaria is accompanied by angioedema, which is a deeper swelling in the layers of the skin. This swelling often affects the face, lips, tongue, throat, hands, and feet. Angioedema can be more painful than itchy and, if it affects the throat, can lead to difficulty breathing, which is a medical emergency.
Fast-Acting Treatments for Urticaria Relief
When hives appear suddenly, the primary goal is to achieve rapid relief from the itching and discomfort. Several treatment options can help manage the symptoms effectively.
At-Home and Over-the-Counter Remedies
For mild to moderate cases of urticaria, several at-home and over-the-counter treatments can provide quick relief:
- Cool Compresses: Applying a cool compress or taking a cool bath can help soothe the skin and reduce itching and inflammation.
- Anti-Itch Solutions: Adding colloidal oatmeal or baking soda to a lukewarm bath can also help alleviate itching.
- Loose-Fitting Clothing: Wearing soft, loose-fitting cotton clothing can minimize skin irritation.
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines are often the first line of medical treatment for hives. Newer, non-drowsy antihistamines like cetirizine and loratadine are generally preferred. They work by blocking the effects of histamine, thereby reducing itching and the rash.
- Topical Creams: Calamine lotion or a mild hydrocortisone cream can be applied to the skin to help with itching.
Medical Interventions for Severe or Persistent Cases
If home remedies and over-the-counter medications are not effective, or if the hives are severe, it is important to seek medical advice. A doctor may recommend:
- Prescription Antihistamines: Stronger antihistamines or a combination of different types may be prescribed. In some cases, a doctor might recommend increasing the dosage of a non-drowsy antihistamine.
- Corticosteroids: For severe outbreaks, a short course of oral corticosteroids like prednisone can be very effective in reducing inflammation. However, these are generally used for a limited time due to potential side effects.
- Epinephrine: In cases where urticaria is part of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) that causes difficulty breathing, an injection of epinephrine is necessary.
A survey across five European countries found a diagnosed-CSU prevalence of 0.92% in adults (EU5: France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK)
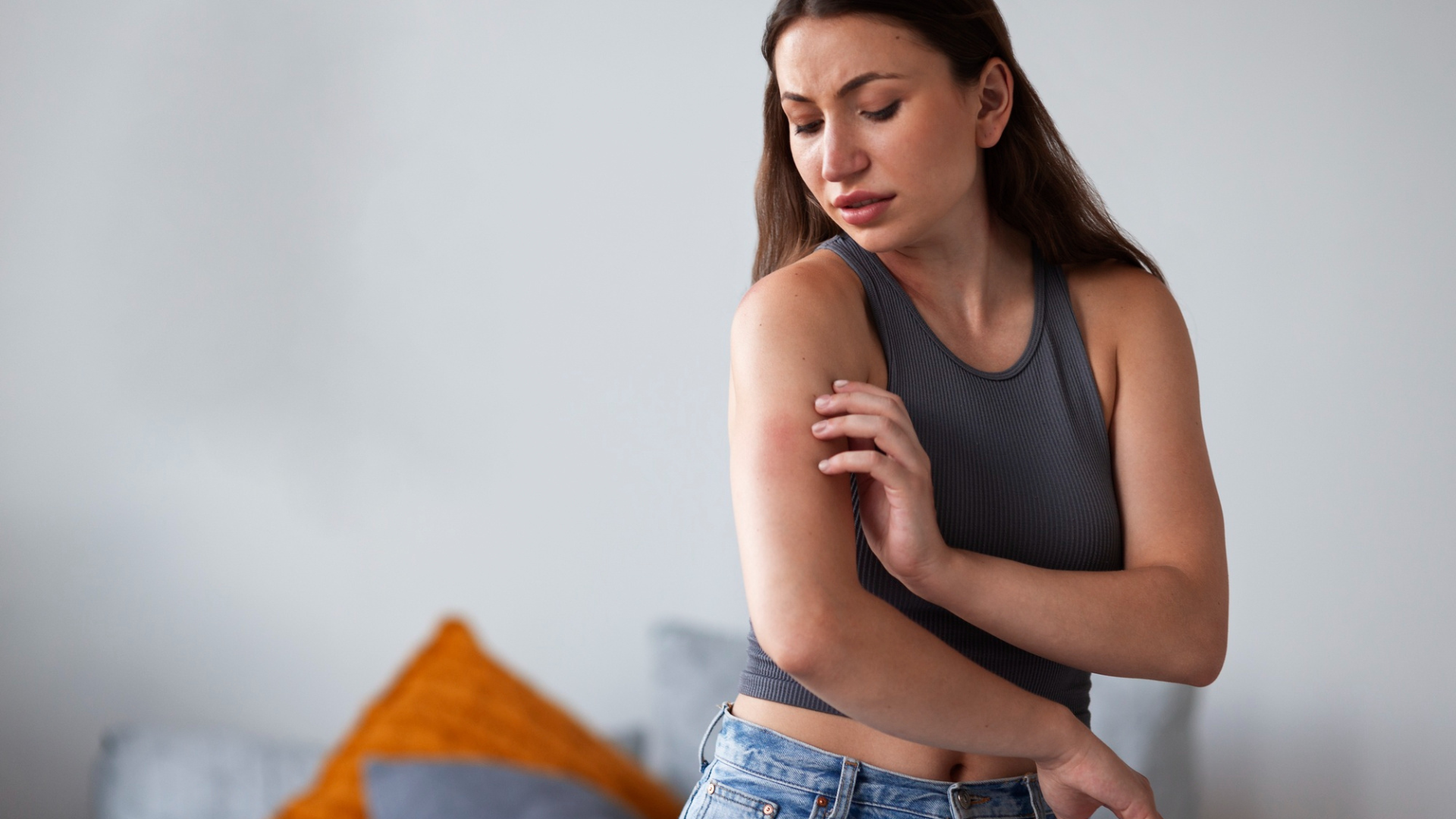

Preventing Future Outbreaks
Once the immediate symptoms are under control, the focus shifts to preventing future episodes of urticaria. This often involves identifying and avoiding the triggers. Keeping a diary of activities, foods eaten, and any new medications can be helpful in pinpointing the cause. If an allergy is suspected, an allergist can perform tests to identify specific allergens.
Living with the unpredictability of sudden urticaria can be challenging. However, understanding the potential causes and having a plan for rapid treatment can make a significant difference. While many cases of acute hives resolve quickly with simple measures, persistent or severe symptoms warrant professional medical attention. For those in need of specialized care, considering a consultation for Urticaria Treatment in Coimbatore can provide access to expert diagnosis and a personalized management plan to keep your skin calm and comfortable.
